Unveiling The Mysteries Of The Rainforests Food Web: A Journey Through Nature's Complex Interactions
Imagine stepping into a lush, vibrant rainforest where every rustle of leaves and chirp of birds tells a story of survival and connection. The rainforests food web is more than just a system—it's a living, breathing tapestry of life that binds every creature, from the tiniest insect to the largest predator. As we dive deeper, you'll discover how this intricate network sustains life and why it matters to all of us.
Now, let's be real here. When you think about rainforests, you probably picture towering trees, exotic animals, and vibrant colors. But there's so much more happening beneath the surface. The food web in rainforests is like a hidden superhighway of energy and nutrients that keeps everything ticking. It's the reason why rainforests are some of the most biodiverse places on Earth, and we're about to break it all down for you.
So, buckle up because we're going on a wild ride through the layers of the rainforest. From producers to predators, every piece of this puzzle plays a crucial role in maintaining balance. And if you're wondering why this matters, stick around. The rainforests food web isn't just about animals and plants—it's about us, too.
- Christmas Background Blurry Transform Your Festive Vibes
- Fishers Indiana Downtown A Thriving Hub Of Culture Community And Innovation
What Exactly is the Rainforests Food Web?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. The rainforests food web is essentially a map of who eats whom in the rainforest ecosystem. It’s not just a simple line of predator and prey; it’s more like a spider web where every strand connects one organism to another. This web ensures that energy flows from one level to the next, keeping the whole system alive and kicking.
Think of it like this: producers, like plants and trees, are at the bottom. They soak up sunlight and turn it into food through photosynthesis. Then come the primary consumers—herbivores like insects and small mammals that munch on these plants. Next up are the secondary consumers, predators that feed on the herbivores. And finally, you have the apex predators at the top, like jaguars or eagles, that keep the population of smaller animals in check.
Why is the Food Web Important in Rainforests?
Here's the deal: the rainforests food web is crucial for maintaining biodiversity. Without it, the entire ecosystem could collapse. For example, if a predator like a jaguar disappears, the population of herbivores might explode, leading to overgrazing and destruction of plant life. This domino effect can disrupt the balance and harm countless species.
- Sodapop Girlfriend The Ultimate Guide To Navigating This Sweet Trend
- Number To Come The Future Is Bright And Its All About Numbers
Plus, the rainforests food web plays a big role in global climate regulation. Healthy ecosystems store carbon, produce oxygen, and influence weather patterns. So, when we talk about preserving the food web, we're also talking about safeguarding our planet's health.
Key Players in the Rainforests Food Web
Now that we know what the food web is, let's meet the main characters. In any rainforest, you'll find a diverse cast of organisms that make this web work. Here's a quick rundown:
- Producers: Plants, trees, and algae. They create the foundation of the food web by converting sunlight into energy.
- Primary Consumers: Herbivores like insects, sloths, and monkeys. They feed directly on plants.
- Secondary Consumers: Small predators like snakes, birds, and frogs. They prey on herbivores.
- Apex Predators: Top-tier hunters like jaguars, harpy eagles, and anacondas. They control the populations of smaller animals.
Each of these groups has a unique role to play, and together, they create a harmonious system that supports life in the rainforest.
How Energy Flows Through the Food Web
Energy in the rainforests food web moves in a specific direction, starting with the sun. Plants absorb sunlight and use it to produce glucose, which becomes food for herbivores. When herbivores eat plants, they transfer some of that energy to predators when they're hunted. However, not all energy is passed on—some is lost as heat or waste at each level.
This flow of energy is vital because it ensures that resources are distributed efficiently. Without this process, the rainforest would struggle to sustain its incredible biodiversity.
Layers of the Rainforest and Their Role in the Food Web
Did you know that rainforests are divided into distinct layers, each with its own set of inhabitants? These layers influence the food web in fascinating ways. Let's take a closer look:
- Emergent Layer: Home to large trees and birds of prey. Apex predators like eagles rule this zone.
- Canopy Layer: Dense with leaves and inhabited by monkeys, insects, and birds. This is where most of the action happens.
- Understory Layer: Shady and filled with smaller plants. Frogs, snakes, and insects thrive here.
- Forest Floor: Dark and damp, it's where decomposers like fungi and insects break down dead matter.
Each layer contributes to the food web, creating a complex network of interactions that keeps the rainforest thriving.
Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Rainforest
Let's give it up for the decomposers! While they might not be the most glamorous creatures, they're absolutely essential. Fungi, bacteria, and insects like termites break down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients back into the soil. This process ensures that the rainforest remains fertile and productive.
Without decomposers, the rainforest would be a mess of rotting matter, and the food web would grind to a halt. So, next time you see a mushroom or a termite, remember they're doing some serious heavy lifting for the ecosystem.
Threats to the Rainforests Food Web
Unfortunately, the rainforests food web faces numerous threats. Deforestation, climate change, and illegal hunting are just a few of the challenges it must contend with. These issues can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem, leading to cascading effects that harm countless species.
For instance, deforestation removes trees, which are the primary producers in the food web. This loss of habitat can lead to the extinction of many species, breaking the links in the web. Similarly, climate change can alter weather patterns, affecting plant growth and animal behavior.
How Can We Protect the Rainforests Food Web?
The good news is that there are steps we can take to protect the rainforests food web. Conservation efforts, sustainable practices, and global cooperation can make a big difference. Here are a few ideas:
- Support organizations working to protect rainforests.
- Choose products that are sustainably sourced.
- Reduce your carbon footprint to combat climate change.
- Spread awareness about the importance of rainforests.
Every little action counts, and together, we can make a positive impact on the future of rainforests.
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of the Rainforests Food Web
Let's look at a couple of real-life examples that illustrate the importance of the rainforests food web. In the Amazon rainforest, jaguars play a crucial role as apex predators. By controlling the populations of smaller animals, they help maintain the balance of the ecosystem. Similarly, in the Congo Basin, elephants act as gardeners, dispersing seeds and creating clearings that allow new plants to grow.
These examples show how every species, no matter how small, contributes to the health of the rainforest. When one piece of the web is removed, the whole system feels the impact.
Scientific Studies on the Rainforests Food Web
Research conducted by organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute provides valuable insights into the workings of the rainforests food web. Scientists use advanced technology to study animal behavior, track population trends, and analyze ecological data.
These studies highlight the intricate relationships between species and emphasize the need for conservation. By understanding the food web better, we can develop strategies to protect it more effectively.
The Importance of Biodiversity in the Rainforests Food Web
Biodiversity is the spice of life in the rainforest. The more diverse the species, the more resilient the food web becomes. This diversity ensures that if one species declines, others can step in to fill its role, maintaining the balance.
For example, if a particular type of fruit-eating bird disappears, other birds or mammals might start eating that fruit, preventing its seeds from going to waste. This adaptability is key to the survival of the rainforest ecosystem.
How Biodiversity Benefits Humans
Here's the kicker: biodiversity in the rainforests food web benefits humans, too. Rainforests provide us with clean air, fresh water, and medicinal plants. They also help regulate the global climate, which affects weather patterns worldwide.
By protecting the biodiversity of rainforests, we're not just saving animals and plants—we're securing our own future. It's a win-win situation.
Future Prospects for the Rainforests Food Web
Looking ahead, the future of the rainforests food web depends on the choices we make today. If we continue down the path of destruction, the web will weaken, and many species will be lost forever. But if we take action to protect rainforests and promote sustainability, we can ensure their survival for generations to come.
Technological advancements, such as remote sensing and AI, can aid in monitoring and managing rainforest ecosystems. These tools can help scientists track changes in the food web and respond quickly to threats.
What Can You Do?
So, what's your role in all of this? You can make a difference by supporting conservation efforts, reducing your environmental impact, and educating others about the importance of rainforests. Every action, no matter how small, contributes to the greater goal of preserving the rainforests food web.
Conclusion: Why the Rainforests Food Web Matters
In conclusion, the rainforests food web is a marvel of nature that sustains life in some of the most vibrant ecosystems on Earth. It's a complex system that requires our respect and protection. By understanding its importance and taking steps to conserve it, we can ensure that rainforests continue to thrive.
So, what are you waiting for? Share this article with your friends, leave a comment below, and let's start a conversation about how we can protect the rainforests food web. Together, we can make a difference!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is the Rainforests Food Web?
- Key Players in the Rainforests Food Web
- Layers of the Rainforest and Their Role in the Food Web
- Threats to the Rainforests Food Web
- Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of the Rainforests Food Web
- The Importance of Biodiversity in the Rainforests Food Web
- Future Prospects for the Rainforests Food Web
- Conclusion: Why the Rainforests Food Web Matters
- Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Rainforest
- How Energy Flows Through the Food Web
- Cleanest City In Us Discovering Americas Green Havens
- Quaaludes Effects The Truth About This Controversial Drug You Need To Know
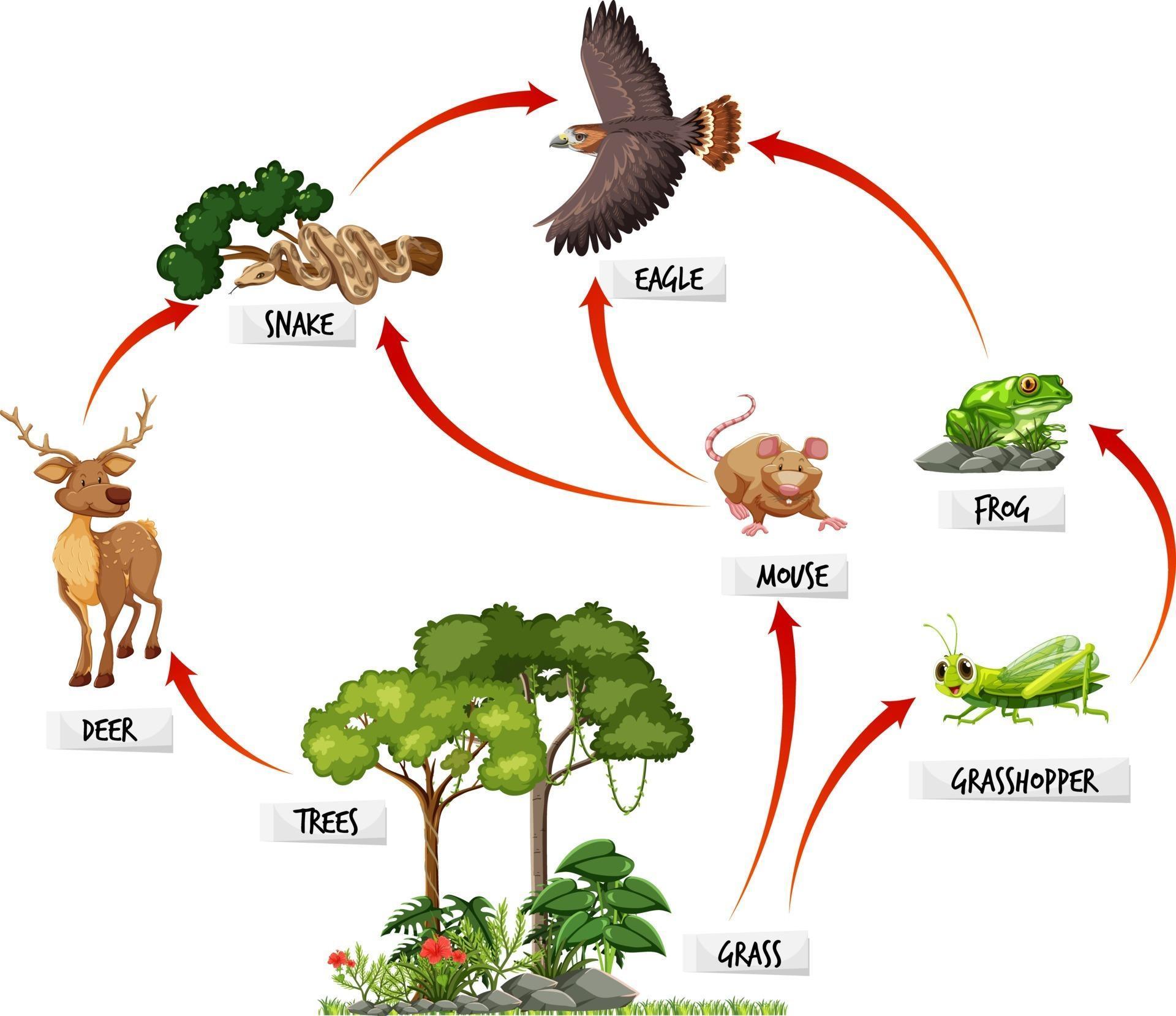
Diagram showing food web in the rainforest 2978464 Vector Art at Vecteezy

Diagram showing food web in the rainforest Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
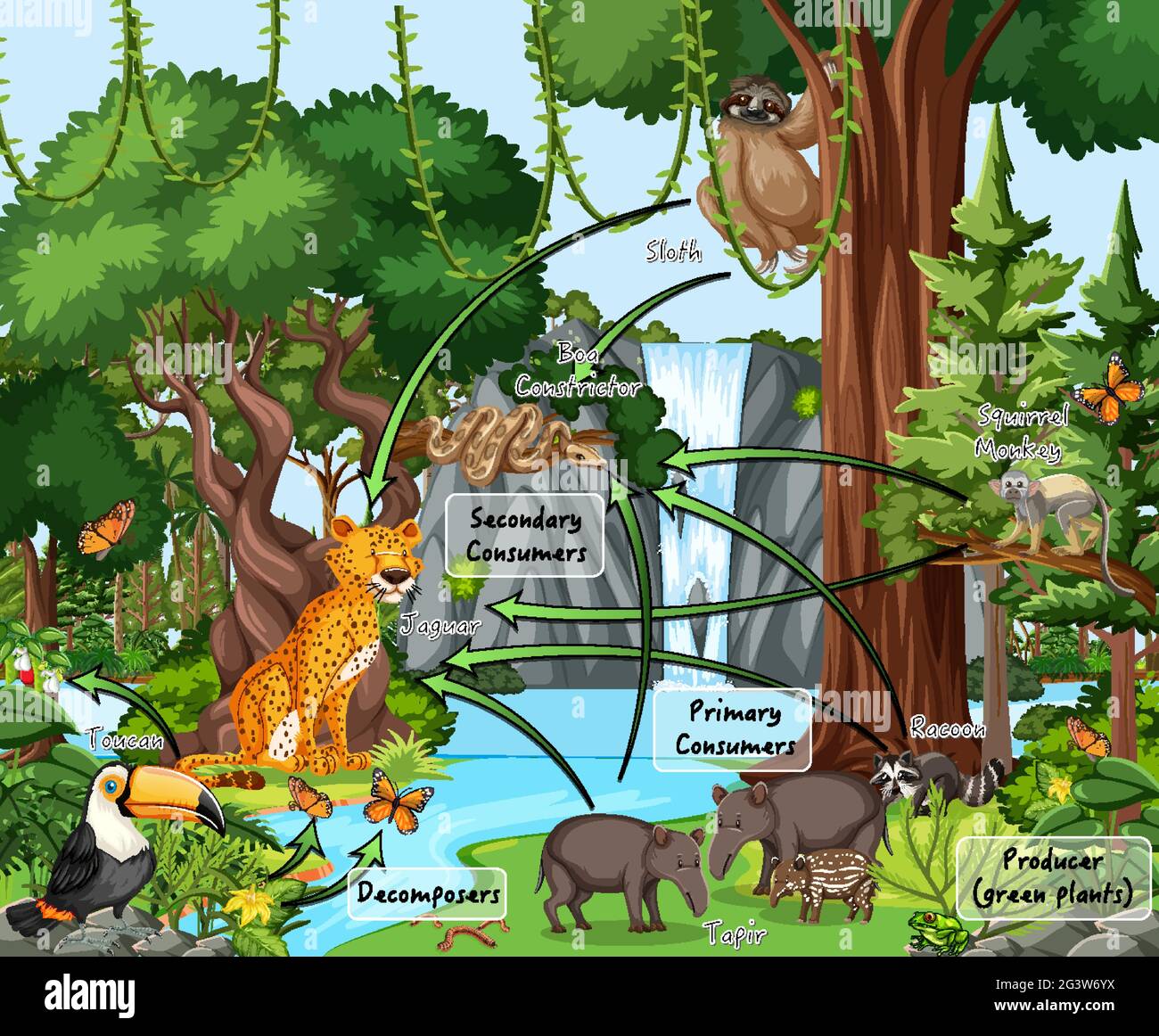
Diagram showing food web in the rainforest illustration Stock Vector