Feudal Society Definition: A Deep Dive Into History's Hierarchy
Feudal society definition is a concept that shaped the medieval world, creating a complex web of power, loyalty, and land ownership. Imagine a time when kings ruled with an iron fist, but they didn’t do it alone. Feudalism was the backbone of medieval Europe, a system where everyone had their place, from the noble lords to the peasants working the fields. It’s like a giant pyramid where everyone depends on each other, but not all positions are created equal. So, buckle up as we dive into this fascinating system that defined centuries of human history.
Now, let’s talk about why feudal society matters today. Even though it’s been centuries since the last knight rode his horse or the last lord claimed his title, the principles of feudalism still resonate in modern governance, economics, and even corporate structures. Understanding this system gives us a clearer picture of how power dynamics work, and it’s like peeling back the layers of an onion—each layer revealing something new and intriguing.
Feudal society wasn’t just about lords and vassals; it was a way of life that influenced every aspect of medieval existence. From the castles perched on hilltops to the villages nestled in the valleys, every part of society played a role in this grand design. So, whether you’re a history buff, a curious mind, or just someone who loves unraveling the mysteries of the past, this article will take you on a journey through the heart of feudal society.
- Food Lion Louisburg Your Onestop Grocery Shop For Freshness And Savings
- Top Spots For Food Lovers The Best Places To Eat In Owatonna
What Exactly is Feudal Society?
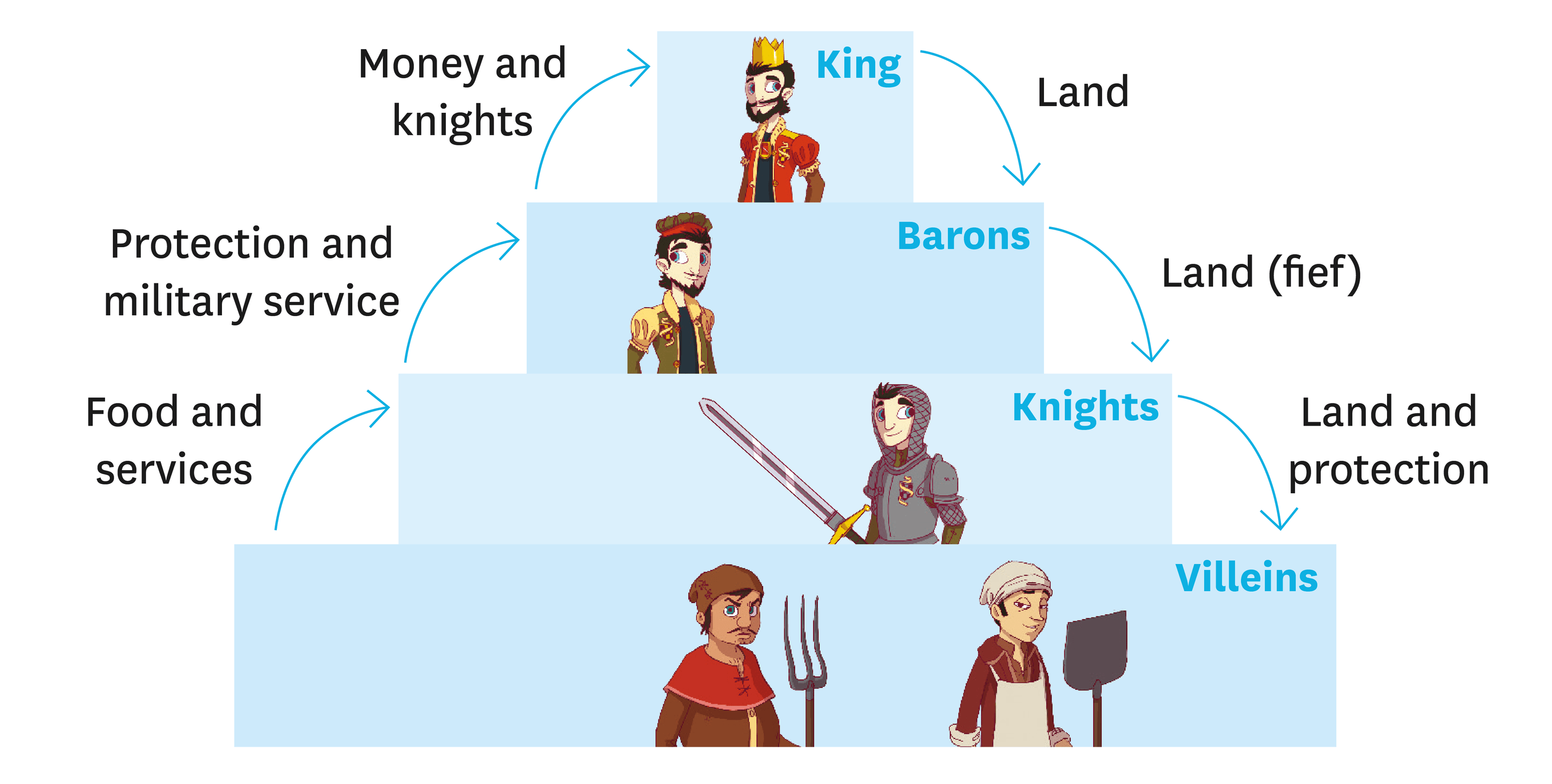
Let’s break it down. Feudal society is basically a system where land ownership equals power. Think of it like this: the king is at the top, and he gives chunks of land, called fiefs, to his loyal nobles. These nobles, or lords, then promise to protect the king and provide military service when needed. But wait, there’s more! The lords, in turn, give smaller pieces of land to knights, who pledge their loyalty and protection. At the bottom of the pyramid are the peasants, who work the land and keep the whole system running. It’s like a giant game of chess, where every piece has its role.
Key Features of Feudal Society
Here’s a quick rundown of what makes feudal society tick:
- Land is the ultimate currency.
- Vassals swear oaths of loyalty to their lords.
- The system is hierarchical, with clear roles for everyone.
- Knights provide military service in exchange for land.
- Peasants work the land but have little say in decision-making.
It’s a system built on mutual obligations, but don’t get me wrong—it’s not all sunshine and rainbows. The lower you are in the hierarchy, the harder life gets. But hey, that’s history for you—full of complexities and contradictions.
- Whats The Golden Birthday Discover The Sweetest Celebration Of The Year
- Los Angeles Best Fast Food Your Ultimate Guide To Musttry Eats
Origins of Feudal Society
So, how did this whole system come about? Well, it didn’t just appear out of thin air. Feudal society started taking shape in the early medieval period, around the 9th century, after the fall of the Roman Empire. With no central authority to keep things in check, local lords began consolidating power. They needed protection, and the best way to get it was by creating a network of alliances based on land and loyalty. It was like building a house of cards, but instead of cards, they used swords and castles.
Impact of the Roman Empire’s Fall
The collapse of the Roman Empire left a power vacuum that feudalism filled. Without a strong central government, local rulers had to fend for themselves. They established their own armies, built fortifications, and formed alliances. It was survival of the fittest, and feudalism was the perfect system for that kind of world. Imagine a bunch of warlords carving up the map, each one trying to outdo the other. That’s the kind of chaos that feudal society brought order to, even if it was a chaotic kind of order.
Feudal Society Structure
Let’s take a closer look at the different layers of feudal society. It’s like a cake with multiple layers, each one stacked on top of the other. At the very top, you’ve got the king, who holds all the power. Below him are the nobles, who own large chunks of land and command armies. Then come the knights, who serve as the military backbone of the system. And finally, at the bottom, you’ve got the peasants, who do all the hard work but get the least reward. It’s a system that’s both fascinating and frustrating, depending on which side of the fence you’re on.
The Role of Knights
Knights were more than just warriors; they were the glue that held the system together. They pledged their loyalty to their lords in exchange for land and protection. It was a win-win situation, at least for them. Knights were expected to uphold a code of chivalry, which meant protecting the weak, serving their lords faithfully, and being honorable in battle. Of course, not all knights lived up to these ideals, but the concept was there, and it added a layer of romance to the harsh realities of feudal life.
Economy in Feudal Society
Money wasn’t the main currency in feudal society; land was. The economy revolved around agriculture, with peasants farming the land to produce food and other goods. Lords collected taxes in the form of crops or labor, and they used this wealth to maintain their estates and support their knights. It was a self-sustaining system, but it wasn’t without its flaws. The lower classes often struggled to make ends meet, and famines were a constant threat. Still, for all its problems, feudal society managed to keep the wheels of the medieval world turning.
Challenges in Feudal Economy
One of the biggest challenges in feudal society was maintaining balance. If the harvest failed, the whole system could collapse. Lords needed their peasants to produce enough food to feed everyone, but they also had to keep enough in reserve for tough times. It was a delicate dance, and not everyone was graceful. Some lords were ruthless, squeezing every last drop of labor from their peasants, while others were more compassionate, understanding that a happy workforce was a productive one.
Feudal Society and Social Mobility
Now, here’s the thing about feudal society: social mobility wasn’t exactly a thing. Once you were born into a certain class, it was hard to move up the ladder. Peasants stayed peasants, and nobles stayed nobles. But there were exceptions. A peasant could rise to become a knight if he proved himself in battle, and a knight could become a lord if he was particularly successful. It was like a medieval version of the American Dream, but with a lot more swords and armor.
Exceptions to the Rule
Some individuals managed to break the mold. Take, for example, William the Conqueror, who started as a duke and became a king. His story is a testament to the fact that, while feudal society was rigid, it wasn’t impossible to change your stars. Of course, it took a lot of skill, ambition, and a bit of luck, but it could be done. It’s like saying, “Hey, the odds are against you, but if you’re willing to fight for it, anything’s possible.”
Feudal Society in Different Regions
Feudal society wasn’t just a European thing; it popped up in other parts of the world too. Japan, for instance, had its own version of feudalism, with samurai playing the role of knights and daimyos acting as lords. Even in the Middle East, there were similar systems of land ownership and military service. It’s like the idea of feudalism was floating around in the air, waiting for someone to grab it and make it their own.
Comparing European and Japanese Feudalism
While both European and Japanese feudalism revolved around land and loyalty, there were key differences. In Japan, the samurai code of bushido emphasized honor and discipline, while in Europe, chivalry was the guiding principle. The architecture was different too, with Japanese castles being more functional and less ornate than their European counterparts. It’s like two cultures taking the same idea and running with it in different directions.
Decline of Feudal Society
Nothing lasts forever, and feudal society was no exception. By the late medieval period, the system began to crumble. The rise of centralized governments, the spread of commerce, and the invention of gunpowder all played a role in its decline. Kings started taking back power, and the need for knights diminished as armies became more professional. It was the end of an era, but it paved the way for new systems and ideas.
Factors Contributing to the Fall
Several factors contributed to the decline of feudal society. The Black Death wiped out a significant portion of the population, disrupting the labor force. The Hundred Years’ War drained resources and weakened noble families. And as trade expanded, money became more important than land. It was like feudalism was a ship that had sailed its course, and it was time to steer in a new direction.
Legacy of Feudal Society
Even though feudal society is long gone, its legacy lives on. Modern governance, especially in parliamentary systems, owes a debt to feudalism’s emphasis on contracts and mutual obligations. Corporate structures, with their hierarchies and divisions of labor, also bear a resemblance to feudal systems. It’s like history has a way of repeating itself, with new twists and turns along the way.
Lessons from Feudalism
So, what can we learn from feudal society? For one, it shows us the importance of balance in any system. Too much power in the hands of a few can lead to oppression, while too little can result in chaos. It also teaches us about the value of loyalty and the dangers of greed. Feudalism may have been flawed, but it was a system that worked for centuries, and that’s something worth thinking about.
Conclusion
In conclusion, feudal society definition isn’t just about a system of land and loyalty; it’s about the human experience. It’s about how people organize themselves, how they create order out of chaos, and how they adapt to changing circumstances. Whether you see it as a relic of the past or a precursor to modern systems, there’s no denying its impact on history. So, the next time you read about knights in shining armor or lords in towering castles, remember that they were part of a world that shaped our own.
And hey, if you enjoyed this deep dive into feudal society, don’t forget to leave a comment or share the article. Who knows? Maybe you’ll inspire someone else to explore the fascinating world of history. After all, history isn’t just about the past; it’s about understanding the present and shaping the future.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is Feudal Society?
- Origins of Feudal Society
- Feudal Society Structure
- Economy in Feudal Society
- Feudal Society and Social Mobility
- Feudal Society in Different Regions
- Decline of Feudal Society
- Legacy of Feudal Society
- Lessons from Feudalism
- Conclusion
- Florida Governors History A Journey Through Leadership And Legacy
- Lourdes Mexican Grill Where Flavor Meets Tradition

feudalism Definition, Examples, History, & Facts Britannica

Feudalism Pyramid Printablegood for interactive notebook Historia
What Was The Feudal System