Divine Right: A Deep Dive Into The Concept That Shaped History
Ever wondered why some rulers in history claimed they were untouchable? The concept of divine right has been around for centuries, influencing politics, religion, and society. It’s not just a fancy phrase; it’s a powerful idea that shaped kingdoms and empires. So, buckle up because we’re about to take a trip down memory lane to explore the divine right like never before.
Imagine a world where kings and queens ruled not because of elections or public opinion, but because they believed they were chosen by a higher power. Sounds wild, right? Well, that’s exactly what the divine right is all about. This belief gave monarchs the ultimate authority, making them untouchable and unchallengeable in their realms. It’s a fascinating concept that still sparks debates today.
Now, let’s dive into the nitty-gritty. We’ll explore what divine right truly means, its historical significance, and how it impacted societies around the globe. But don’t worry, we’ll keep it real, engaging, and packed with juicy details. So, if you’re ready to uncover the secrets behind this age-old doctrine, let’s get started!
- Sephora Donations Where Glamour Meets Generosity
- Number To Come The Future Is Bright And Its All About Numbers
Here's the roadmap of what we'll cover:
- What is Divine Right?
- Historical Background
- Divine Right in Religion
- Divine Right in Politics
- Impact on Society
- Criticism and Controversy
- Modern Perspective
- Divine Right Around the World
- Key Figures Associated with Divine Right
- Conclusion
What is Divine Right?
Let’s start with the basics. Divine right, in a nutshell, is the belief that monarchs are chosen by God to rule. This idea suggests that kings and queens have a sacred duty to govern their people, and no one, not even the most powerful nobles, can question their authority. It’s like they got a golden ticket to leadership straight from the heavens.
This concept was often used to justify absolute monarchy, where rulers had unchecked power. Think of it as a divine seal of approval that made rebellion not only politically risky but also spiritually blasphemous. It’s a pretty neat trick if you think about it, turning earthly authority into something almost supernatural.
- Kendrick Beating His Wife Uncovering The Truth Behind The Controversy
- Sept 19 Zodiac Sign Unlocking The Mysteries Of Virgo And Libra
Key Features of Divine Right
- Rulers derive their authority directly from God.
- Challenging the ruler is seen as defying divine will.
- It supports the idea of absolute monarchy, where the king or queen has ultimate control.
But here’s the thing—divine right wasn’t just a European thing. Versions of this belief popped up in different cultures throughout history, each with its own twist. So, while the core idea remained the same, the way it was applied varied depending on the time and place.
Historical Background
To truly understand divine right, we need to look back at its roots. The idea has been around for centuries, with traces found in ancient civilizations. In Egypt, pharaohs were considered gods in human form, and in Mesopotamia, kings were seen as divine representatives on Earth.
Fast forward to medieval Europe, and divine right became a cornerstone of political theory. Monarchs like Louis XIV of France famously declared, “L’État, c’est moi” (I am the state), reinforcing their divine mandate to rule. This period saw the rise of absolute monarchies across the continent, with rulers using divine right as a tool to consolidate power.
How Divine Right Evolved Over Time
Over the centuries, the concept of divine right adapted to changing circumstances. In the Middle Ages, it was used to justify feudal hierarchies, where kings ruled over lords, who in turn governed the peasants. As societies became more complex, divine right evolved to address new challenges, but its core message remained the same: rulers were chosen by God and must be obeyed without question.
Divine Right in Religion
Religion played a huge role in shaping the divine right doctrine. In Christianity, for example, texts like Romans 13:1 were often cited to support the idea that all authority comes from God. This made it easier for monarchs to argue that their rule was divinely sanctioned.
But it wasn’t just Christianity. In Hinduism, the concept of "divine kingship" was prevalent, with rulers seen as manifestations of deities. Similarly, in ancient China, emperors were considered the "Sons of Heaven," linking their authority to celestial approval.
Religious Texts Supporting Divine Right
- Romans 13:1 – “Let every person be subject to the governing authorities, for there is no authority except from God.”
- Hindu scriptures often refer to kings as embodiments of Vishnu or other gods.
- Chinese philosophy emphasized the Mandate of Heaven, which justified imperial rule.
These religious foundations gave divine right a powerful boost, making it harder for subjects to question their rulers without also challenging their faith.
Divine Right in Politics
Politically speaking, divine right was a game-changer. It allowed monarchs to rule without worrying about pesky things like public opinion or parliamentary approval. Kings could make decisions based on what they believed was God’s will, rather than what their subjects wanted.
This system had its pros and cons. On one hand, it provided stability and centralized power, which could be beneficial during turbulent times. On the other hand, it also led to abuses of power, as rulers sometimes acted with impunity, believing they were above the law.
Examples of Divine Right in Action
- King James I of England famously argued that kings were God’s lieutenants on Earth.
- In France, the divine right doctrine was used to justify the absolutist policies of the Bourbons.
- In Japan, the emperor was seen as a living god, giving his rule a divine aura.
These examples show how divine right influenced political systems across the globe, shaping the way leaders governed and interacted with their subjects.
Impact on Society
The impact of divine right on society was profound. It created a clear hierarchy, with the monarch at the top and everyone else below. This structure influenced everything from social interactions to economic policies.
However, it also stifled innovation and progress. Since questioning the ruler was akin to questioning God, people were less likely to challenge the status quo. This led to a lack of political reform and social mobility in many societies.
Social Consequences of Divine Right
- Reinforced social hierarchies, making it difficult for lower classes to advance.
- Discouraged political dissent, leading to authoritarian rule.
- Shaped cultural norms, emphasizing obedience and loyalty to the ruler.
Despite these drawbacks, divine right also fostered a sense of unity and shared identity, as people believed they were part of a divine order.
Criticism and Controversy
Not everyone was on board with the divine right doctrine. Critics argued that it gave rulers too much power, often at the expense of their subjects. Philosophers like John Locke challenged the idea, advocating for more democratic forms of government.
Over time, these criticisms gained traction, leading to movements like the Enlightenment, which emphasized reason and individual rights over divine authority. The American and French Revolutions were direct challenges to the divine right of kings, paving the way for modern democratic systems.
Key Critics of Divine Right
- John Locke – Argued for natural rights and limited government.
- Voltaire – Satirized the divine right doctrine in his writings.
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau – Advocated for the social contract over divine authority.
These thinkers helped shift the conversation away from divine right and towards more inclusive forms of governance.
Modern Perspective
In today’s world, divine right might seem like a relic of the past. However, its legacy lives on in various forms. Some modern leaders still use religious rhetoric to justify their authority, while others draw inspiration from the idea of divine sanction in more secular ways.
But the concept also serves as a reminder of how far we’ve come. Modern democracies prioritize the will of the people over divine mandate, ensuring that leaders are accountable to their citizens rather than claiming divine approval.
Lessons from Divine Right
- Power should be checked and balanced to prevent abuse.
- Leaders should be accountable to their people, not just to a higher power.
- Progress often comes from questioning established norms and traditions.
These lessons are as relevant today as they were centuries ago, reminding us of the importance of critical thinking and reform.
Divine Right Around the World
While divine right is often associated with Europe, it has roots in many other cultures. From the pharaohs of Egypt to the emperors of Japan, the idea of divine rulership has taken many forms. Each culture added its own unique twist, creating a rich tapestry of beliefs and practices.
For example, in Africa, some traditional rulers were seen as intermediaries between the gods and their people. In the Americas, indigenous leaders often had spiritual roles, blurring the line between political and religious authority.
Cultural Variations of Divine Right
- In Africa, rulers were often seen as divine intermediaries.
- In the Americas, spiritual leadership was closely tied to political power.
- In Asia, divine right was often linked to religious doctrines and philosophies.
These variations show how adaptable the concept of divine right could be, shaping societies in unique and fascinating ways.
Key Figures Associated with Divine Right
Throughout history, many figures have been closely associated with the divine right doctrine. Here are a few notable ones:
| Name | Role | Notable Achievements |
|---|---|---|
| Louis XIV of France | King | Established absolute monarchy in France. |
| King James I of England | King | Wrote extensively on divine right theory. |
| Emperor Meiji of Japan | Emperor | Reinforced the divine status of the Japanese emperor. |
These leaders used divine right to consolidate their power and shape their nations in lasting ways.
Conclusion
Divine right has been a powerful force in history, shaping politics, religion, and society. While its influence has waned in modern times, its legacy continues to resonate in various ways. By understanding this concept, we gain insight into how past societies operated and how far we’ve come in terms of governance and human rights.
So, the next time you hear someone talk about divine right, remember the rich history behind it. It’s more than just an old idea; it’s a reflection of humanity’s ongoing struggle to balance power, authority, and accountability.
Now, it’s your turn. What do you think about divine right? Do you believe it still has relevance today? Leave a comment below or share this article with your friends. Let’s keep the conversation going!
- Gators And Florida State A Deep Dive Into The Rivalry History And More
- Capricorn Best Matches In Zodiac Unlocking The Secrets Of Cosmic Compatibility
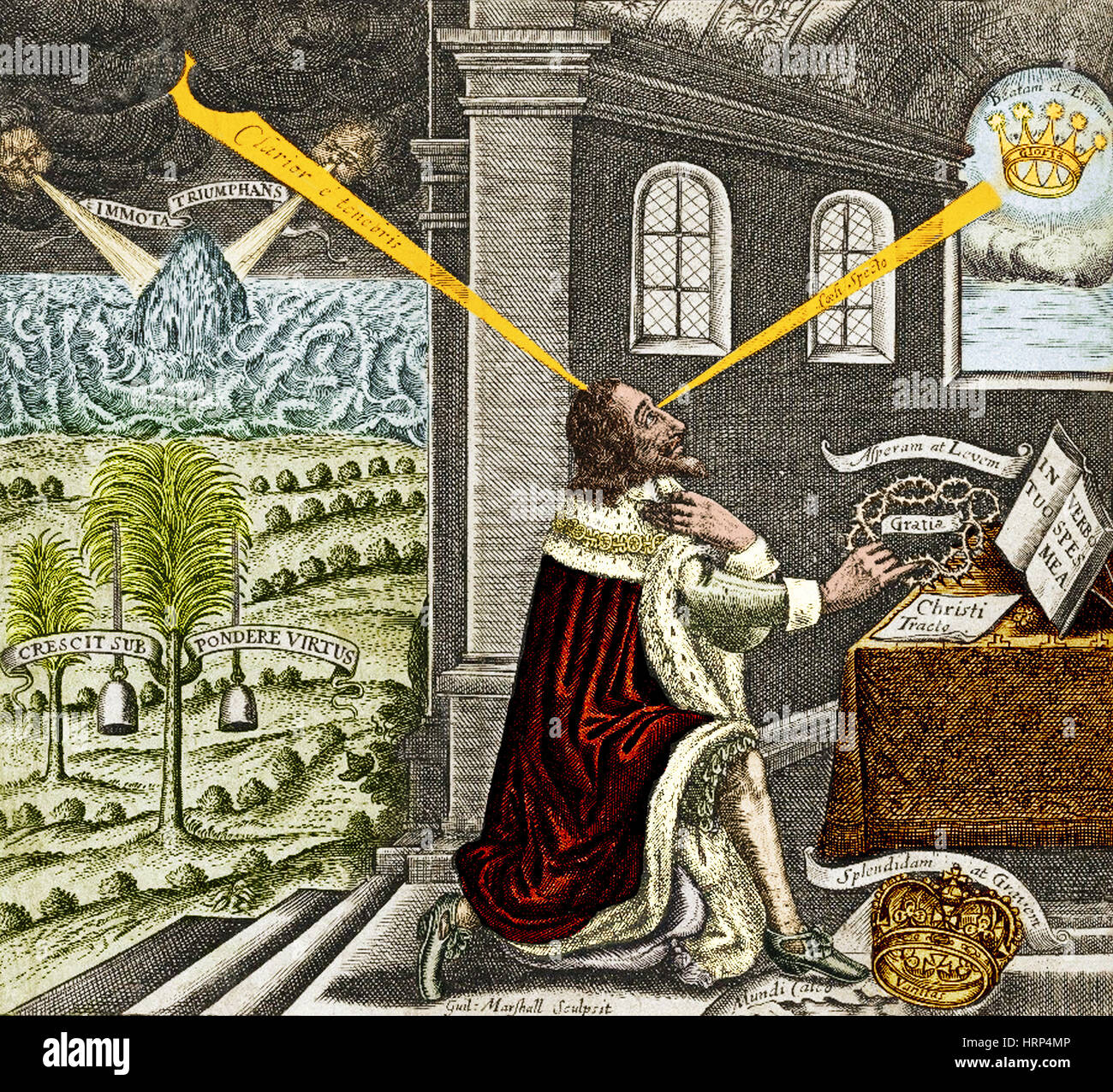
Divine Right Theory Of Kingship

Divine Right Of Kings Stock Photo, Royalty Free Image 56704113 Alamy

The Divine Right of Kings or Regal Tyranny? (Hobbes and Lilburne